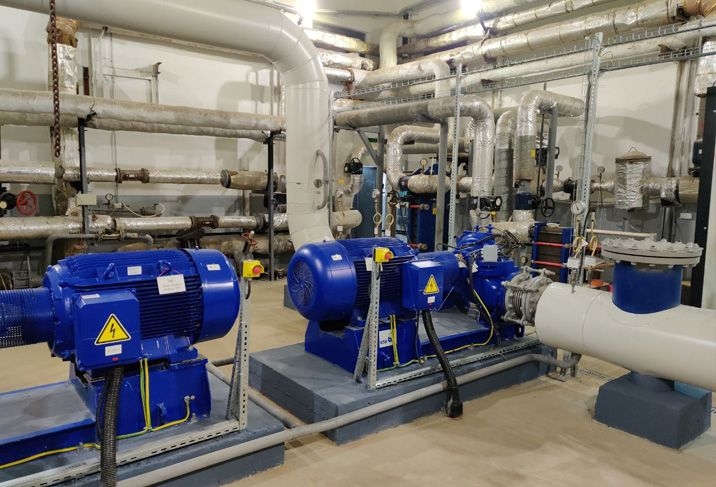
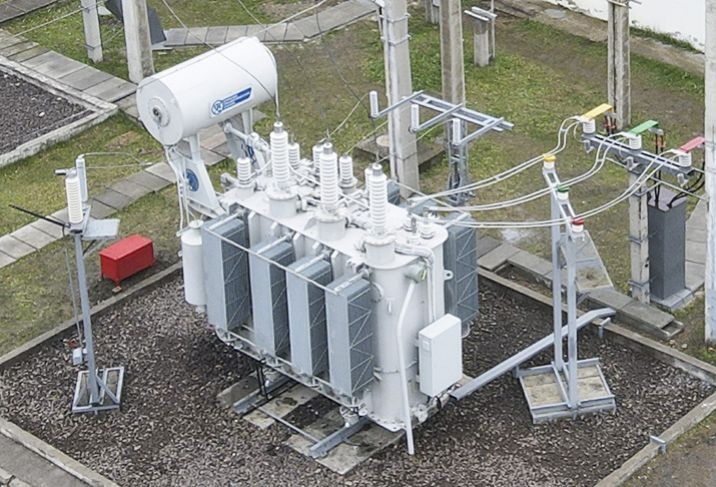
Horus Energy company offers replacement and modernization services for steam turbines of various capacities. The technical and economic indicators of the proposed turbines according to the characteristics of the flow parts show the efficiency at the level of leading world manufacturers. We guarantee the operability of turbines for more than 40 years and the overhaul period of at least 6 years.
What is steam turbine?
A steam turbine is a device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. The steam turbine is a form of heat engine that derives much of its improvement in thermodynamic efficiency from the use of multiple stages in the expansion of the steam, which results in a closer approach to the ideal reversible expansion process.
Working principle of steam turbine.
Working principle of steam turbine depends on the dynamic action of steam. A high-velocity steam is coming from the nozzles and it strikes the rotating blades which are fitted on a disc mounted on a shaft. This high-velocity steam produces dynamic pressure on the blades in which blades and shaft both start to rotate in the same direction. Basically, in a steam turbine pressure energy of steam extracts and then it converted into kinetic energy by allowing the steam to flow through thew nozzles. The conversion of kinetic energy does mechanical work to the rotor blades and the rotor is connected to a steam turbine generator which acts as a mediator. Turbine generator collects mechanical energy from the rotor and converts into electrical energy. Since the construction of steam turbine is simple, its vibration is much less than the other engine for same rotating speed. Though different types of governing system are used to improve turbine speed.
Types of steam turbines.
Most modern steam turbines consist of several cylinders. Most often, two- and three-cylinder turbines are used. The three-cylinder turbine consists of high, medium and low pressure cylinders. In a two-cylinder, the last two are combined into one. There are also turbines with a large number of cylinders.
Depending on the nature of the thermal process, steam turbines are divided into 3 main groups:
- Condensing - without adjustable steam extraction. This type of turbine is most often used in thermal power plants;
- Heating plants - with adjustable selections. These turbines are used in combined heat and power plants, where part of the steam is used to heat the network water used for heating and hot water supply to nearby settlements;
- Special purpose turbines - crushed (throttled) steam turbines, two-pressure turbines and upstream (foreshalt).
The main parameters of the nominal values.
- Nominal power of the turbine - the maximum power that the turbine must develop for a long time at the terminals of the electric generator, at normal values of the main parameters or when changing them within the limits agreed upon by industry and state standards. A turbine with adjustable steam extraction can develop power above the nominal if it meets the conditions for the strength of its parts.
- Economic power of the turbine - the power at which the turbine operates with the greatest efficiency. Depending on the parameters of fresh steam and the purpose of the turbine, the rated power can be equal to economic or 10–25% more.
- Nominal temperature of regenerative heating of feed water - temperature of feed water after the last pre-heater.
- Nominal cooling water temperature — The temperature of the cooling water when entering the condenser.
Reliability indicators.
High reliability and cost-effectiveness of the proposed steam turbines are provided by:
- Aerodynamic experimental tests of the blades, confirming both their reliability and effectiveness;
- Smooth meridional contours of the flowing part;
- Inspection of blade design by CFD methods;
- Three-dimensional profiling of guide vanes;
- Optimization of steam inlets, taps and exhausts by CFD methods;
- New advanced seal designs;
- Introduction of modern progressive design methods, as well as technologies and equipment from leading manufacturers.
Due to the use of highly economical blading, modern types of seals, developed dehumidification in the design of the low-pressure flow part, as well as a developed system of regenerative heaters, a significant reduction in losses is achieved. The working blades of all stages are performed with all-milled bandages, which increases the reliability and operational characteristics of the stages.