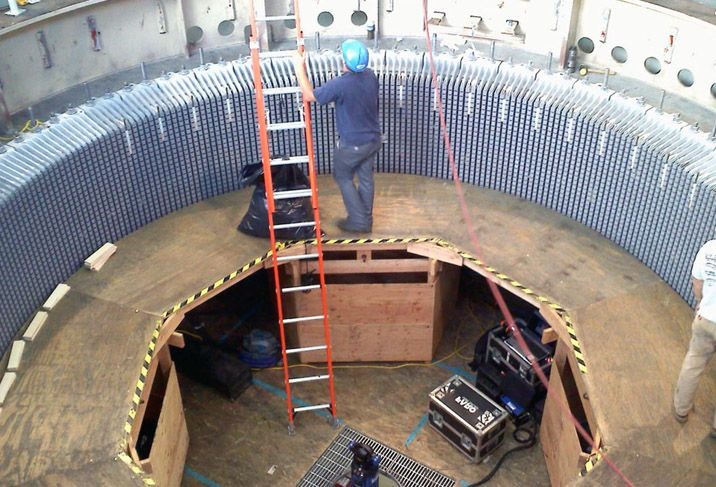
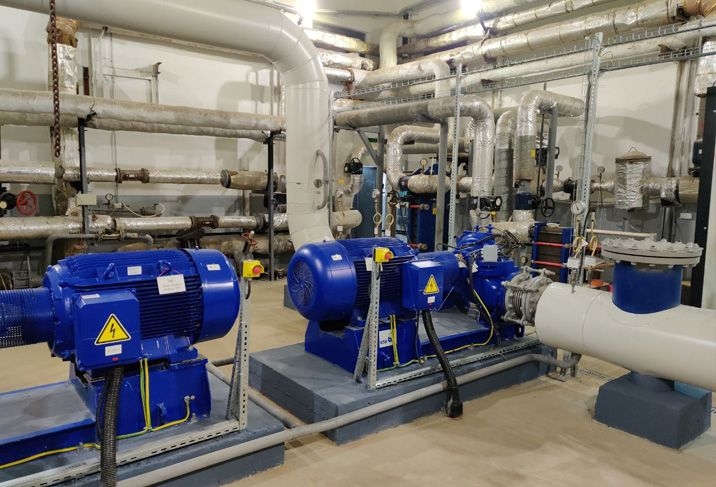
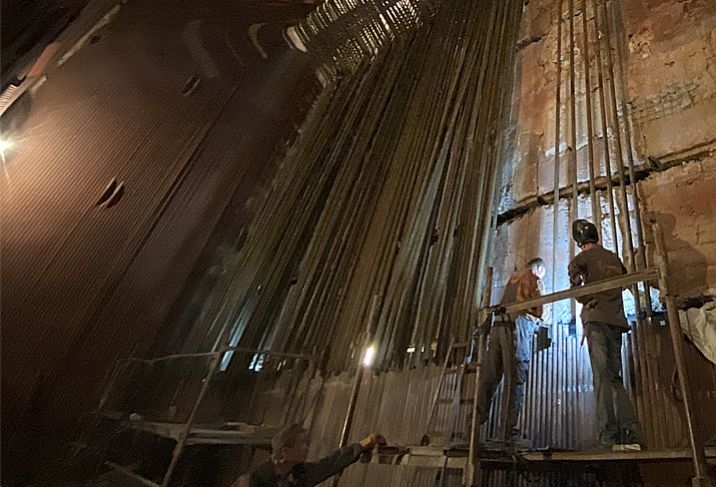
Компания «Horus Energy» предлагает услуги по модернизации гидрогенераторов. Предлагаемые гидрогенераторы отличаются доступностью элементов конструкции для монтажа и обслуживания, высокой надежностью, повышенным фактическим ресурсом, ремонтопригодностью и экологической безопасностью.
Что такое гидрогенератор?
Гидрогенератор — устройство, состоящее из электрического генератора и гидротурбины, выполняющей роль механического привода, предназначен для выработки электроэнергии на гидроэлектростанции.
Электрический генератор — устройство, в котором неэлектрические виды энергии (механическая, химическая, тепловая) преобразуются в электрическую энергию.
Обычно генератор гидротурбинный представляет собой синхронную явнополюсную электрическую машину вертикального исполнения, приводимую во вращение от гидротурбины, хотя существуют и генераторы горизонтального исполнения (в том числе капсульные гидрогенераторы).
Конструкция генератора в основном определяется параметрами гидротурбины, которые в свою очередь зависят от природных условий в районе строительства гидроэлектростанции (напора воды и её расхода). В связи с этим для каждой гидроэлектростанции обычно проектируется новый генератор.
Генераторы гидротурбинные обычно имеют сравнительно малую частоту вращения (до 600 об/мин) и достаточно большой диаметр (до 20 м), чем в первую очередь определяется вертикальное исполнение большинства генераторов, так как при горизонтальном исполнении становится невозможным обеспечение необходимой механической прочности и жёсткости элементов их конструкции.
Вертикальные генераторы гидротурбинные обычно состоят из следующих основных частей:
- Статор;
- Ротор;
- Верхняя крестовина;
- Нижняя крестовина;
- Подпятник (упорный подшипник, который воспринимает вертикальную нагрузку от вращающихся частей гидрогенератора и гидротурбины);
- Направляющие подшипники.
По особенностям конструкции генераторы гидротурбинные подразделяются на подвесные и зонтичные. У подвесных генераторов подпятник располагается над ротором на верхней крестовине, у зонтичных подпятник располагается под ротором в нижней крестовине или опирается на крышку гидротурбины (в этом случае верхняя крестовина у генератора отсутствует).
На гидроаккумулирующих электростанциях используются обратимые генераторы (генераторы-двигатели), которые могут как вырабатывать электрическую энергию, так и потреблять её. От обычных генераторов они отличаются особой конструкцией подпятника, позволяющей ротору вращаться в обе стороны.
Горизонтальные капсульные гидрогенераторы представляют собой часть герметичной капсулы, содержащей помимо генератора гидротурбину и системы обеспечения. Капсула помещается непосредственно в проточную часть гидроэлектростанции.
Показатели надёжности.
Высокие показатели экономичности и надежности гидрогенераторов обеспечиваются благодаря применению современных материалов и технологий.
Применение современных материалов:
- Материалы для термореактивной изоляции обмоток статоров;
- Современные марки электротехнических сталей для изготовления сердечников статоров;
- Современные лаки на эпоксидной основе;
- Немагнитные нажимные щеки полюсов ротора;
- Фторопластовое покрытие для сегментов подпятника и подшипника.
Применение современных технологий:
- Вакуумно-нагнетательная пропитка полюсов ротора;
- Пайка обмоток возбуждения;
- Лазерная резка сегментов обода ротора;
- Сборка сердечника статора «в кольцо» на месте установки с применением предварительной горячей растяжки сердечника статора.
При проектировании и исследовании применяются современные средства расчета, включающие в себя компьютеризацию расчетов с применением современных вычислительных пакетов, а также компьютеризацию проектных чертежей.
Основные типы предлагаемых гидрогенераторов:
- Вертикальные гидрогенераторы с косвенным воздушным охлаждением мощностью до 420 МВт;
- Вертикальные гидрогенераторы с водяным охлаждением обмоток статоров для ГЭС мощностью до 720 МВт;
- Капсульные гидрогенераторы для ГЭС мощностью до 54 МВт с форсированным воздушным охлаждением;
- Быстроходные гидрогенераторы на номинальную частоту вращения до 750 об/мин;
- Гидрогенераторы для малых ГЭС мощность более 4 МВт.